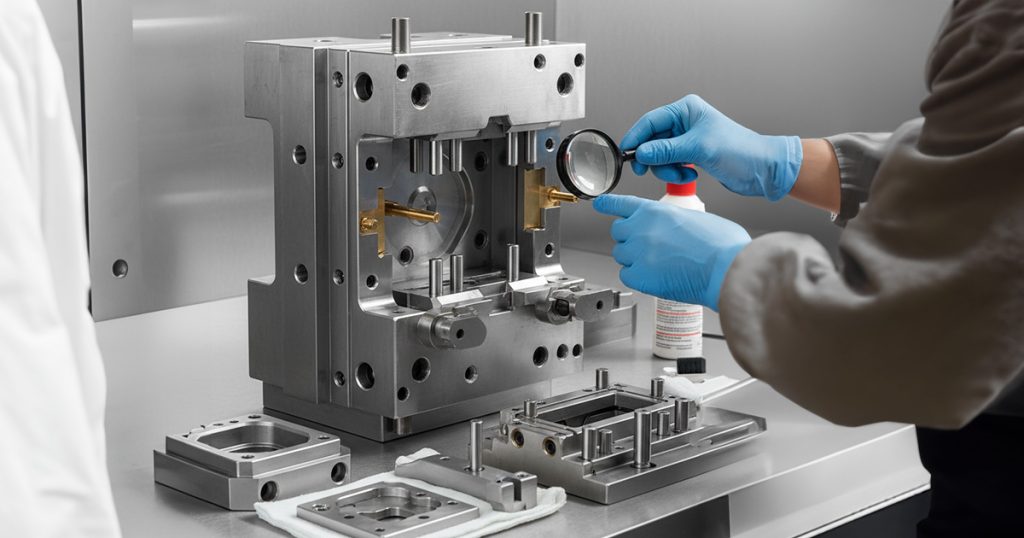
Preventive and Corrective Maintenance for Industrial Injection Molds
The reliability of an injection molding process depends heavily on effective Mold Maintenance, a discipline that ensures molds operate at peak performance during high-volume manufacturing. When properly executed, maintenance strategies help control production costs, extend mold lifespan, and ensure consistent part quality. As molds become more complex, and as cycle times shorten, maintenance is no longer optional—it’s a core engineering requirement for modern factories.
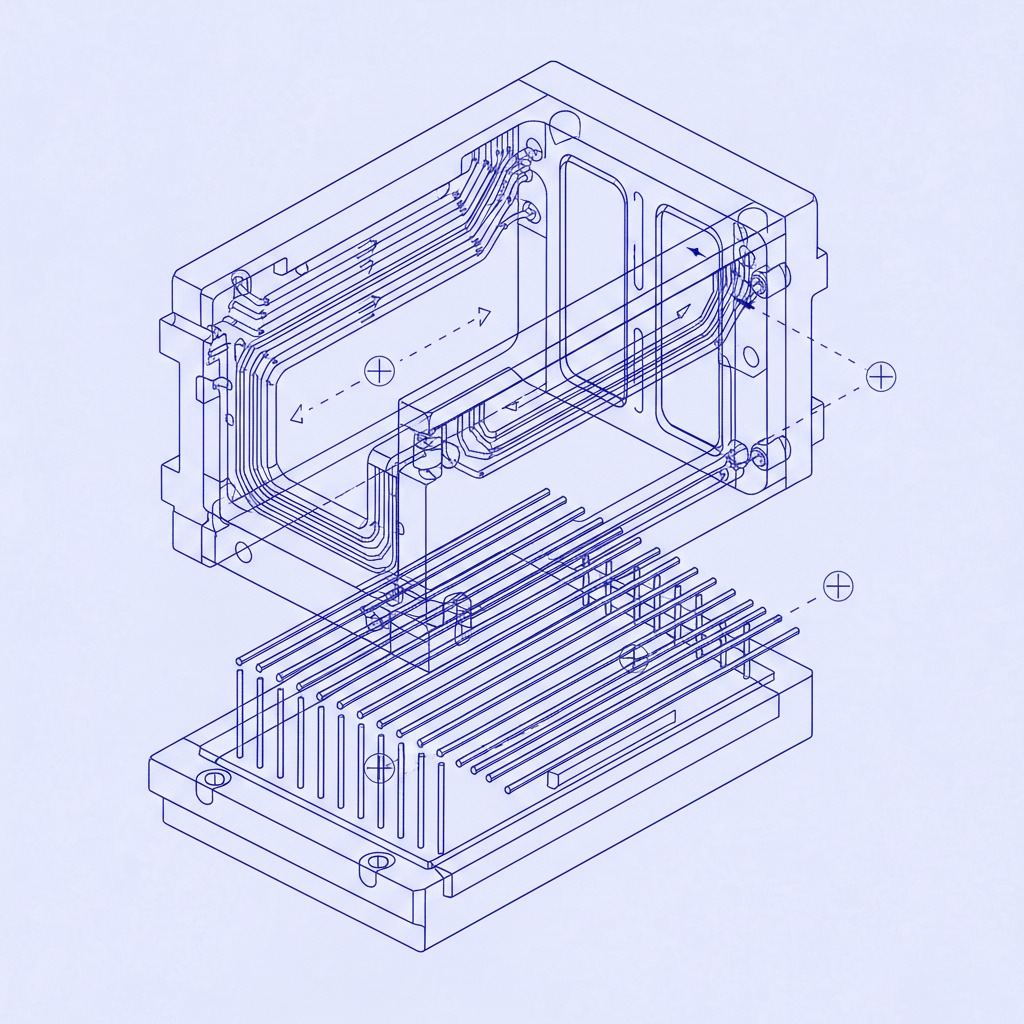
Effective Mold Maintenance goes beyond lubrication or cleaning. It includes diagnostics, part replacement, dimensional verification, cooling system optimization, and corrective interventions that prevent costly failures during production. Manufacturing companies that invest in structured maintenance programs experience reduced downtime, fewer defects, and predictable tooling behavior across long production runs.
The Role of Preventive Mold Maintenance in Industrial Manufacturing
Preventive maintenance is the foundation of long-term mold performance. It focuses on routine interventions designed to stop issues before they cause damage or disrupt production. In high-volume molding environments, preventive Mold Maintenance is applied based on cycles, material type, temperature profiles, or specific part requirements.
Key Tasks in Preventive Maintenance
1. Cleaning and residue removal
Plastic resins—especially those with fillers, additives, or pigments—leave buildup inside cavities, vents, and runners. Preventive Mold Maintenance removes these residues to avoid defects such as burn marks, short shots, flash, and dimensional inconsistencies.
2. Inspection of wear-prone components
Critical areas such as parting lines, ejector pins, guide bushings, slides, lifters, and gate areas require micro-inspections. Even micron-level wear can propagate into major alignment problems if ignored.
3. Cooling channel descaling
Scale buildup inside cooling circuits reduces heat transfer efficiency. Poor temperature control increases cycle time and accelerates mold wear. Preventive descaling maintains stable and predictable cooling performance.
4. Lubrication and anti-corrosion treatment
High-temperature lubricants ensure smooth mechanical movement of components such as ejectors and slides. Anti-corrosion coatings protect molds during storage or downtime.
5. Dimensional verification
Metrology tools—CMMs, laser scanners, and pin gauges—monitor long-term dimensional stability. Preventive Mold Maintenance uses these measurements to anticipate failures before they occur.
This proactive approach significantly reduces corrective interventions, boosts uptime, and increases mold lifespan—critical benefits for manufacturers targeting high production efficiency.
Corrective Mold Maintenance for Restoring Tool Performance
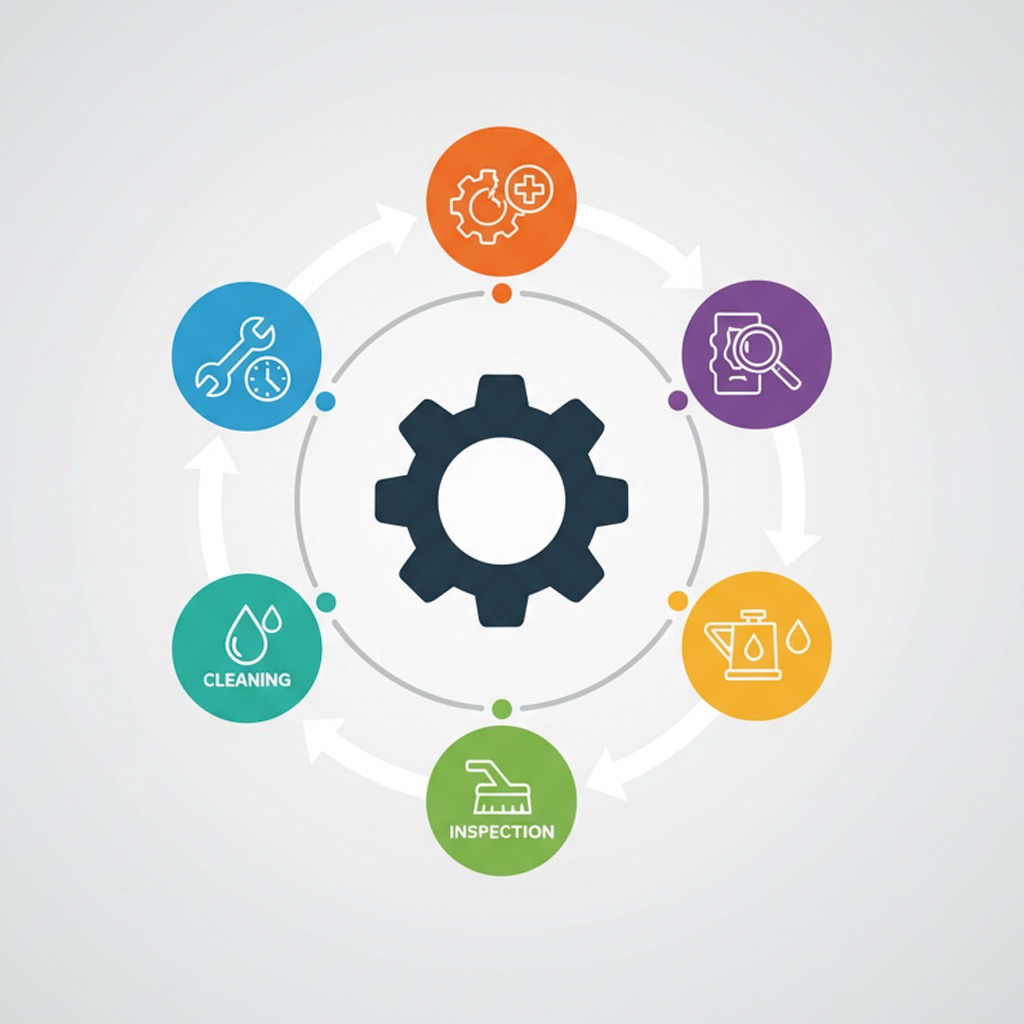

Corrective maintenance is executed when issues appear during production or after a failure has occurred. It focuses on diagnosing the cause, repairing damaged components, restoring functionality, and recalibrating the mold.
Typical Corrective Maintenance Actions
1. Replacement of worn components
Slides, ejector pins, bushings, lifters, and inserts often require replacement due to abrasion, misalignment, or mechanical fatigue.
2. Repair of cavity or core damage
Factors such as material contamination, insufficient lubrication, improper alignment, or trapped debris can damage the molding surface. Skilled technicians restore geometry using welding, polishing, or insert replacement.
3. Thermal imbalance corrections
Incorrect temperature control can cause warpage, welding lines, and excessive shrinkage. Corrective Mold Maintenance involves cleaning channels, repairing leaks, or recalibrating the cooling system.
4. Addressing flash, short shots, or dimensional drift
Common symptoms of mold deterioration include flash at the parting line, incomplete fills, and out-of-tolerance parts. Corrective actions may involve adjusting clamping, sharpening edges, or restoring venting.
Corrective Mold Maintenance ensures molds return to optimal functionality—but it is more expensive and time-consuming than preventive work. This is why professional mold operators aim for a balanced maintenance strategy.
Maintenance Protocols for Maximum Mold Uptime
To achieve world-class performance, maintenance must be systematic and data-driven. Leading manufacturers adopt structured protocols to standardize every step of the Mold Maintenance process.
Essential Maintenance Protocol Components
Maintenance cycles by shot count
Maintenance frequencies are defined by cycles, material type, mold complexity, and operating temperatures.
Digital maintenance logs
Modern factories use software systems to track interventions, predict failures, and schedule maintenance efficiently.
Inspection checklists
A standardized checklist ensures no component goes unnoticed—cavities, cooling channels, venting, ejector systems, and guiding elements are all documented.
Tool history records
Each mold has a complete lifecycle record, enabling better cost forecasting and long-term planning.
Spare-part inventory management
Holding essential components—pins, bushings, inserts—prevents long production stoppages.
Through these structured practices, companies achieve reduced downtime, controlled maintenance costs, and longer mold service life.
Why Mold Maintenance Matters for Production Quality
Consistent maintenance ensures dimensional accuracy, part repeatability, surface finish quality, and optimal cycle time. When molds are neglected, defects multiply, cycle times increase, and machine operators must constantly correct settings.
Effective Mold Maintenance guarantees:
Stable cycle times
Lower scrap rates
Predictable production planning
Reduced energy consumption
Longer mold lifespan
Improved product consistency
In an era where quality and speed define competitive advantage, Mold Maintenance becomes a strategic necessity for every injection molding manufacturer.
Conclusion
Preventive and corrective Mold Maintenance ensures injection molds remain reliable, productive, and consistent over long manufacturing cycles. By integrating scheduled inspections, real-time monitoring, and systematic repair strategies, companies protect their tooling investments and maintain high performance across all production lines. Effective mold care is not just maintenance—it’s a key contributor to industrial efficiency and product excellence.
Got questions? Go to our Contact Us page and send us a message — we’re here to help.






