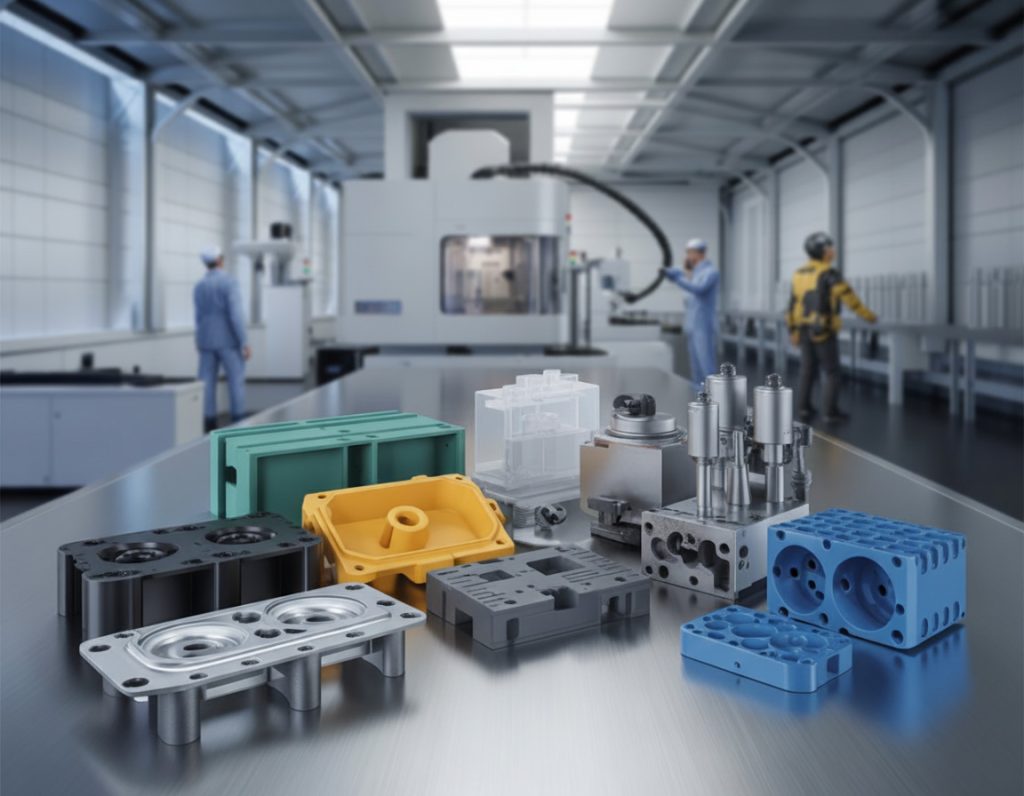
What Is Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a process in which molten thermoplastic material is injected into a mold cavity under controlled pressure and temperature. Once the material cools and solidifies, it takes the exact shape of the mold, producing components that are consistent, durable, and ready for assembly or further processing.
This process is ideal for mass production of complex parts with high repeatability and minimal waste, making it a cost-effective and sustainable solution for various industries.
Sumiparts specializes in the injection of plastic parts for industrial and automotive applications, ensuring precision, durability, and high quality through advanced mold design and CNC machining
Plastic Injection Process:
The plastic injection molding process is a highly controlled manufacturing method designed to produce consistent, high-quality plastic components with complex geometries. It begins with thermoplastic materials—commonly ABS resin, but also polycarbonate, nylon, or polypropylene—being heated until they reach a molten state.
Once the material reaches the ideal temperature and viscosity, it is injected under high pressure into a precision-machined steel or aluminum mold. This mold defines the exact shape, dimensions, and surface finish of the final product. The molten plastic fills every cavity of the mold, ensuring even distribution and structural integrity.
As the material cools and solidifies, it retains the detailed features of the mold. The component is then carefully ejected from the mold, inspected for dimensional accuracy, and—if required—sent for secondary finishing processes such as trimming, polishing, or assembly.
This process provides exceptional repeatability, speed, and cost efficiency, making it ideal for both prototype runs and large-scale production. At SUMIPARTS, every stage of the injection process is optimized through CNC-machined molds, automated controls, and real-time quality monitoring. This guarantees consistent results, reduced material waste, and superior performance across every batch produced.
With the combination of precision engineering and advanced equipment, plastic injection molding delivers parts that meet the strictest industrial and aesthetic standards—from automotive components and electrical housings to custom-designed mechanical parts.
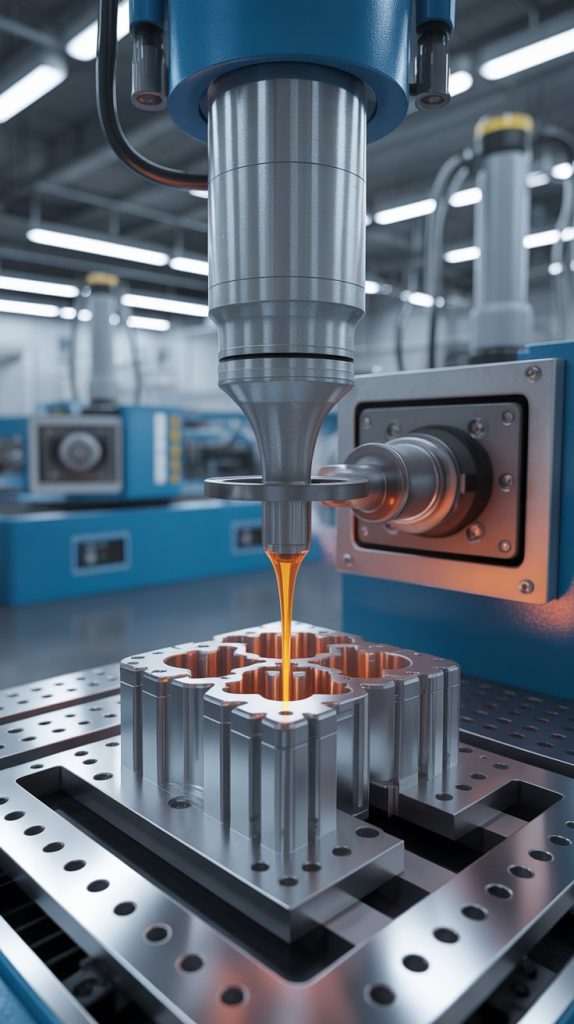

Benefits of Plastic Injection Molding

-
Precision and Consistency:
Injection molding guarantees accuracy and repeatability in every piece, ensuring uniform dimensions across large production volumes. -
Material Efficiency:
The process minimizes material waste thanks to the reuse of thermoplastic residues and optimized mold design. -
Design Flexibility:
It allows the creation of complex geometries, fine details, and lightweight structures that would be difficult to achieve with other methods. -
Scalability:
Once the mold is produced, thousands of identical parts can be manufactured quickly and efficiently, reducing unit costs. -
Surface Finishing Options:
Injection-molded parts can achieve smooth, textured, or polished finishes directly from the mold, eliminating additional surface treatments.
Plastic Injection Molding for Industrial Applications
-
Plastic injection molding is one of the most versatile and efficient manufacturing processes used in the production of plastic components. At SUMIPARTS, we combine advanced technology with years of engineering experience to design and manufacture high-quality molded parts that meet the most demanding industrial standards.
Through precision molding systems and modern injection machines, we ensure that each part meets strict dimensional tolerances, excellent surface finishes, and long-lasting performance.

Considerations:
- Mold Cost: Manufacturing molds is costly, making injection molding more efficient for high-volume production.
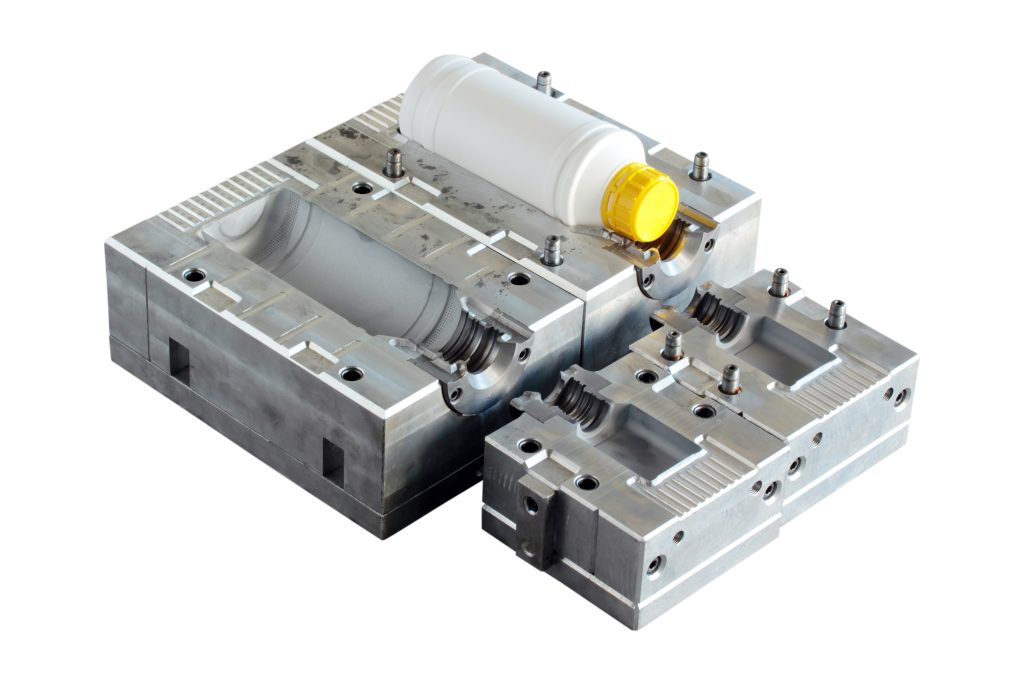
- Product Design: Proper mold design prevents defects like bubbles, burrs, and burn marks.
Materials Used in Plastic Injection
At SUMIPARTS, we work with a wide variety of engineering-grade thermoplastics to ensure the best performance for each application. Common materials include:
Polypropylene (PP): Lightweight, flexible, and resistant to chemical agents.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Strong and durable, ideal for structural parts.
Polycarbonate (PC): Transparent and impact-resistant, used in technical and optical components.
Nylon (PA): High wear resistance, suitable for mechanical parts and gears.
PVC and HDPE: Used for applications that require insulation, flexibility, or chemical resistance.
Each material is selected according to the customer’s functional, mechanical, and environmental requirements.
Industrial Applications
Plastic injection molding is essential in a wide range of industries, including:
Automotive components
Electrical and electronic housings
Industrial equipment and tools
Medical devices
Consumer goods and packaging
At SUMIPARTS, we tailor every project to our client’s needs, ensuring efficiency, durability, and cost optimization at every stage of production.