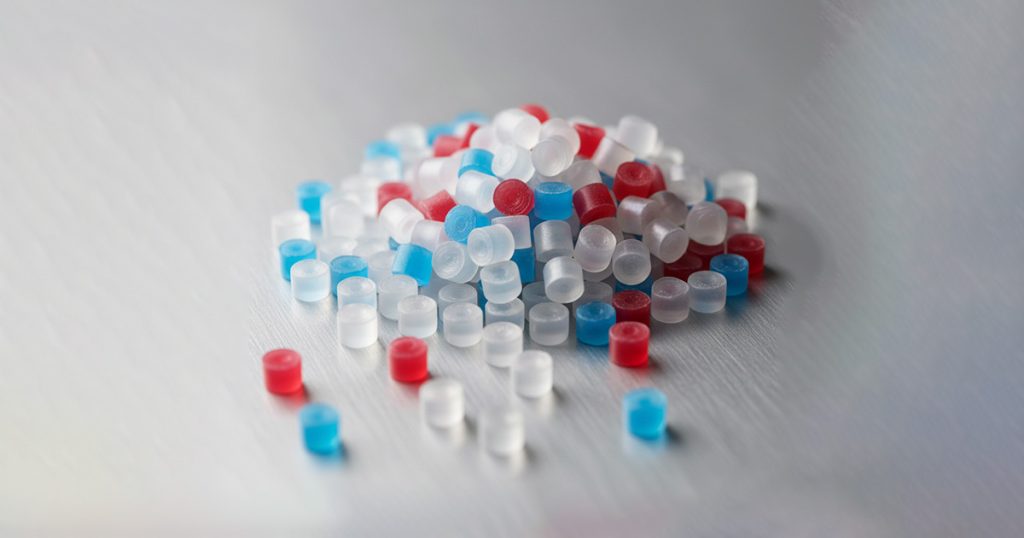
Choosing the Right Plastic Pellets for Injection Molding: A Practical Guide for 2026
The selection of plastic pellets for injection molding is one of the most critical decisions in manufacturing. The type of resin used determines the mechanical properties, dimensional stability, surface finish, cycle time, and long-term performance of the final part. With industries demanding greater customization, sustainability, and precision, choosing the right pellets in 2026 requires a deeper understanding of material science and application-specific requirements.
Injection molding is increasingly used across automotive, electronics, consumer goods, medical devices, and construction sectors. Each industry requires materials with very different characteristics—impact resistance, heat stability, chemical resistance, transparency, flexibility, or dimensional accuracy. This guide explains how to evaluate and select the correct plastic pellets for injection molding based on performance requirements, cost, regulations, and production efficiency.
Understanding the Main Types of Plastic Pellets for Injection Molding
Before choosing a resin, manufacturers must understand the differences between the main families of thermoplastic materials. Each type of pellet offers unique advantages depending on the application.
Commodity Plastics
Used in high-volume, low-cost products.
Common options include:
PP (Polypropylene): Lightweight, chemical resistant, excellent flow.
PE (Polyethylene): Impact resistant, flexible, durable.
PS (Polystyrene): Rigid, clear, low-cost.
Engineering Plastics
Ideal for components requiring high strength, heat resistance, or precision.
Some examples:
ABS: Tough, dimensional stability, great for enclosures.
Nylon (PA): Strong, wear-resistant, good for gears and mechanical parts.
POM (Acetal): Excellent sliding properties and low friction.
High-Performance Plastics
Used for specialized applications in aerospace, medical, or extreme environments.
Examples:
PEEK: Exceptional strength, chemical and thermal resistance.
PPS: High heat stability and dimensional accuracy.
Ultem (PEI): Medical-grade, transparent options, ideal for high heat.
Sustainable & Bio-Based Pellets
A fast-growing segment for 2026.
Options include:
PLA: Compostable materials for consumer goods.
Recycled PP/PE: Suitable for non-structural products.
Bio-based polyamides: Similar strength to nylon with lower carbon footprint.
Understanding these families helps narrow the selection before analyzing application-specific requirements.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Plastic Pellets
Choosing the right plastic pellets for injection molding involves much more than selecting a generic resin type. Engineers and manufacturers must carefully evaluate how these plastic pellets for injection molding behave under specific performance requirements, processing conditions, environmental exposure, and long-term cost efficiency. The mechanical characteristics of plastic pellets for injection molding—such as tensile strength, flexural modulus, impact resistance, creep behavior, and wear or friction performance—directly determine whether the material can withstand real industrial demands. For instance, gears require pellets with exceptional toughness and wear resistance, while structural housings benefit from pellets that offer higher rigidity and dimensional stability.
Thermal behavior is another decisive factor when choosing plastic pellets for injection molding, especially for applications operating near engines, electrical components, or high-heat environments. Engineers must analyze melting temperature, glass transition temperature, and heat deflection limits to ensure the selected pellets maintain stability during operation. Additionally, chemical resistance becomes critical in sectors such as automotive, medical, cleaning systems, and industrial fluids, where plastic pellets for injection molding must withstand moisture, oils, solvents, and acids without degrading.
Aesthetic requirements are equally important. The choice of plastic pellets for injection molding determines color consistency, gloss level, transparency, and the ability to apply or reproduce mold textures and high-quality surface finishes. For regulated industries, these pellets must comply with strict standards such as FDA and USP Class VI for medical devices, UL94 flame-resistance ratings, automotive OEM specifications, and environmental directives like REACH and RoHS.
Processing behavior also plays a major role. The flow characteristics of plastic pellets for injection molding directly influence cycle time, shrinkage levels, cooling behavior, warpage control, and how well complex geometries can be molded. Pellets with optimized melt flow index enable faster cycles and lower energy usage. Conversely, selecting inadequate plastic pellets for injection molding can slow production, cause instability in part quality, increase scrap, and negatively affect overall manufacturing efficiency.
How Material Selection Impacts Cost, Quality, and Performance
Material cost is only one part of the economic equation. The right pellets can reduce manufacturing costs significantly.
Improved Process Efficiency
Materials with good flow reduce injection pressure and energy consumption.
Faster cooling resins reduce cycle time, increasing productivity.
Reduced Scrap and Defects
Pellets with predictable behavior minimize warping, sink marks, voids, and flow lines.
Stable material consistency leads to fewer rejected parts.
Long-Term Performance
The correct resin improves durability and resistance to environmental stress.
Better performance translates into fewer warranty claims and higher customer satisfaction.
Lower Mold Maintenance
Certain filled materials (like glass fiber) can wear out molds faster.
Choosing proper steel and surface treatment is essential when working with abrasive pellets.
Overall, proper selection of plastic pellets for injection molding affects every stage of the project—from mold design to production and final performance.
Trends for 2026 in Plastic Pellet Selection
2026 brings new priorities for the molding industry:
Greater adoption of recycled and bio-based pellets without compromising mechanical strength.
Smart materials with additives for UV resistance, anti-static behavior, or antimicrobial surfaces.
Improved pellet uniformity thanks to AI-driven extrusion control.
High-flow engineering resins that allow thinner walls and faster cycles.
Advanced polymer blends designed for lightweighting in automotive and electronics.
Companies that stay updated with these material innovations gain better competitiveness and production efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing the right plastic pellets for injection molding is essential for achieving optimal quality, performance, and cost-efficiency. By understanding resin types, application requirements, and material behavior during processing, manufacturers can reduce cycle time, improve product reliability, and meet modern industrial standards. As 2026 advances, innovation in material science will continue shaping how injection-molded products are designed and produced.
Got questions? Go to our Contact Us page and send us a message — we’re here to help.






