What Is Plastic Printing and Why It Matters in Modern Manufacturing
Plastic Printing is transforming the way industrial components are designed and produced. It allows manufacturers to move from concept to prototype in a fraction of the time, minimizing waste and optimizing design validation before full-scale production.
Plastic Printing: From Prototyping to Functional Production

Plastic Printing has revolutionized modern manufacturing, allowing rapid prototyping and short-run production with unmatched precision. At Sumiparts, we apply Plastic Printing technologies to transform digital designs into tangible parts, helping our clients validate dimensions, functionality, and ergonomics before entering large-scale production.
Through Plastic Printing, we produce components in materials such as ABS, PLA, PETG, and flexible polymers that simulate the behavior of injected or extruded plastics. This versatility allows for quick iterations, design validation, and cost optimization during the development phase.
Our Plastic Printing service integrates seamlessly with CNC machining and mold manufacturing, ensuring continuity from concept to industrial production. This process accelerates innovation, reduces lead times, and enhances quality in every stage of development.
3D Plastic Printing: From Concept to Prototype
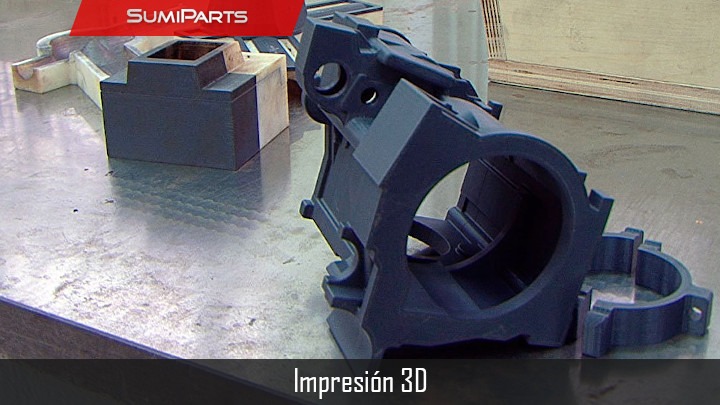
Plastic Printing is a process in which physical objects are created by depositing material layer by layer from a digital model. This technology has revolutionized modern manufacturing, offering countless applications — from medical prostheses and custom accessories to industrial prototypes and research projects. Its versatility and precision make it one of the most valuable tools in current product development.
At Sumiparts SAS, we implement 3D Plastic Printing as a key stage to provide confidence and accuracy in every project. We understand that when developing or designing a new component, questions often arise — Will the part fit correctly? Will the coupling system perform as expected? To address these uncertainties, we use 3D printing as a validation step before large-scale investments in molds or dies.
Through the use of Plastic Printing, we can evaluate all the dimensional and aesthetic aspects of your product design. Although the mechanical properties of a printed prototype differ from the final injected or machined part, it is an ideal alternative to verify design details, dimensions, and overall functionality before production.
Materials Used in Plastic Printing
Today, a wide variety of materials are available for 3D Plastic Printing, each offering unique characteristics to simulate different types of industrial components. Depending on your project’s purpose and testing requirements, prototypes can range from flexible, rubber-like pieces (TPU, TPE) to high-strength, rigid parts made from ABS or Nylon.
Among the most commonly used materials are:
-
PLA (Polylactic Acid): An eco-friendly plastic derived from natural sources such as corn, making it biodegradable and easy to extrude. It operates at lower temperatures than ABS and resists deformation.
-
ABS: A strong, durable plastic ideal for functional parts and industrial testing.
-
TPU/TPE: Flexible elastomers used for soft, rubber-like applications.
-
Nylon: A resistant material with good impact strength and durability.
Applications and Benefits of 3D Printing in Product Development
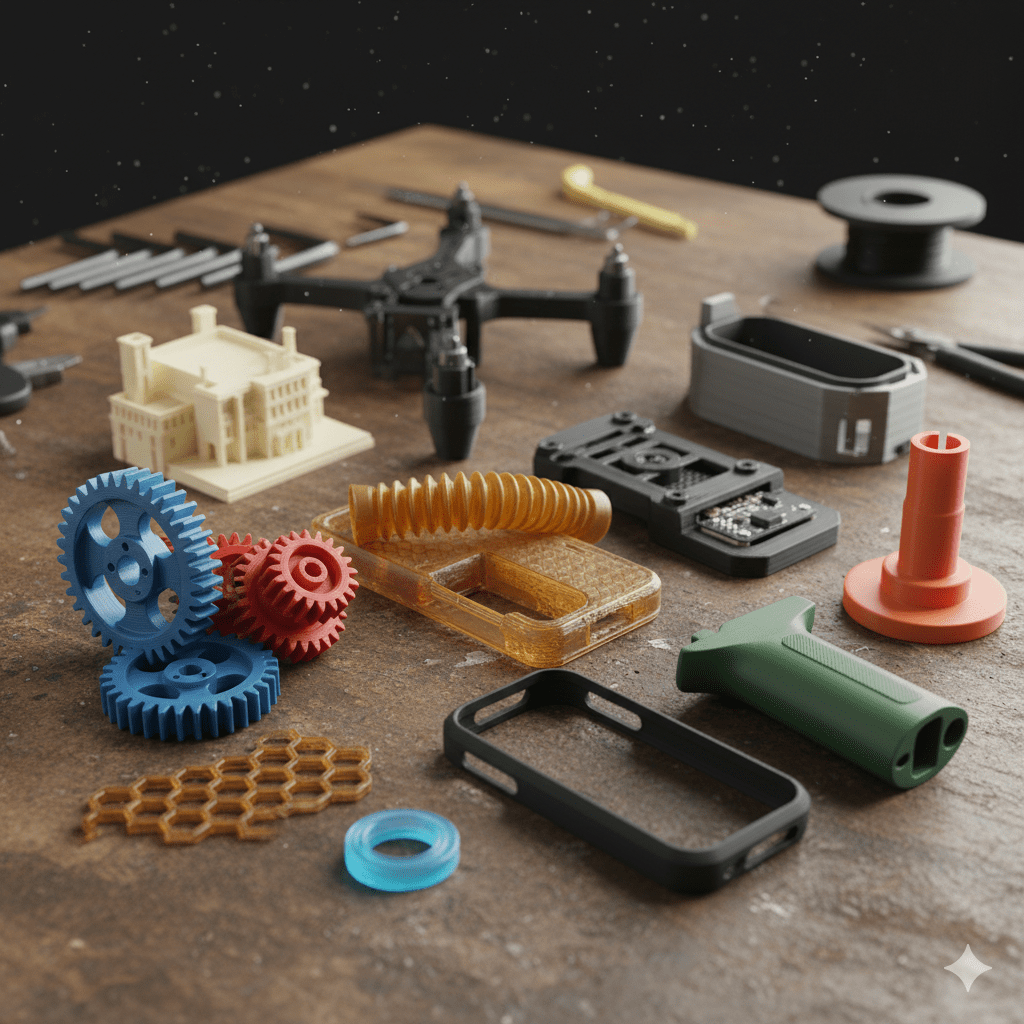

One of the greatest advantages of 3D printing is the ability to explore complex geometries that would be difficult or costly to produce with traditional manufacturing methods. Designers and engineers can create intricate parts, internal channels, or lattice structures that optimize weight, material use, and performance.
3D printing also allows for rapid iteration. Multiple versions of a prototype can be produced in a short time, enabling testing for fit, function, and ergonomics. This iterative process reduces errors and increases confidence in the final design before committing to full-scale production.
Another benefit is the ability to simulate end-use conditions. Prototypes can be subjected to stress tests, temperature changes, or mechanical loads, providing valuable data on how the final product will perform in real-life conditions. These insights help refine designs and make informed decisions about materials, tolerances, and assembly methods.
Additionally, 3D printing enables cost-effective small batch production. For custom parts, short runs, or one-off components, traditional tooling and molds may be too expensive. Using additive manufacturing, companies can produce functional parts with minimal setup, reducing waste and overall production costs.
Finally, the environmental impact is reduced. Since 3D printing deposits material only where it is needed, scrap and excess waste are minimized. Combined with the use of bio-based plastics like PLA or recyclable materials, this makes additive manufacturing a more sustainable alternative for prototyping and small-scale production.
If you want to know more about the 3D PRINTING, at SUMIPARTS we are willing to collaborate with you. We want to provide you with the best services at your reach. Get in touch with us by calling Pbx: +57 748 22 13 Cel: 313 699 13 56 or by sending an email to info@sumiparts.com. Our technical team will be ready to assist you.